What is CNC Laser Cutting?
CNC laser cutting technology is computer numerical control (CNC) equipment capable of cutting holes and intricate shapes with outstanding precision. Laser cutting is a technology designed to produce metal parts from sheet metal through the use of a focused, high-powered laser beam, which vaporizes, melts, burns, or removes material by essentially blowing it away by a jet of gas. This process results in an edge with a high-quality surface finish. This technology, which was initially used for drilling holes into diamond dies, emerged in 1965 and has since been adapted for industrial use and has evolved to be capable of cutting various materials. Laser metal cutting machines cut materials including titanium, aluminum, steel, stainless steel, spring steel, brass, copper, and bronze. CNC laser cutters are also capable of cutting non-metals such as acrylic, textiles, polycarbonate, nylon, laminated fiberglass, polycarbonate, PVC, rubber, and silicone. Given the accuracy and quality of CNC Laser Cutting technology and its success for industrial use, laser cutting technology has been growing in demand in education, business, and architectural sectors, as well as by hobbyists.
How it Works
The laser cutting process involves engraving or cutting sections of materials into various custom shapes. This is achieved most commonly through mirrors or fiber optics. Commercial lasers follow a CNC or G-code of a designated pattern to cut materials with the aid of a motion control system. The basis of laser cutting involves a focused laser beam contacting a workpiece. This enables a laser cutter to cut metallic and non-metallic materials of different material thicknesses using a guided, formed, and bundled laser beam. Electrical discharges or lamps are stimulated with a lasing material within a closed container. Once sufficient energy is reached, it escapes as monochromic light. Mirrors or fiber optics direct the light to a lens, focusing it on the workpiece. The focused beam is commonly less than 0.0125 inches in diameter, though widths as narrow as 0.0004 inches are achievable. The beam is typically fixated and confined to a very tiny spot of a few thousandths of an inch by a lens or a mirror. This allows for intricate contours to be cut precisely, smoothly, and burr-free.
Laser Cutting Procedures
Laser cutting procedures include flame cutting, which is used on mild steel, fusion cutting, the procedure of choice for meltable materials, as well as sublimation cutting, which is used for high-quality cutting edges for fine cutting tasks, and drilling, resulting in holes of various sizes using a non-contact method.
Laser Cutting Methods
Various methods using lasers are available, with each type specialized in cutting different materials. Some of the methods used are melt and blow, thermal stress, vaporization, melt blow and burn, scribing, craving, burning stabilized laser cutting as well as cold cutting.
CNC Laser Cutting Types
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Due to their low cost, CO₂ lasers with higher power levels are utilized for cutting and welding, whereas CO₂ lasers with lower power levels are used for engraving.
Neodymium (Nd) and neodymium yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG)
Nd:YAG lasers are identical in style to their CO₂ laser counterparts, though their function is different. Both lasers can be used for welding, however, Nd:YAG lasers are employed where high power and low repetition are required, as well as for boring and engraving applications.
Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers are solid-state lasers, unlike CO2, which relies on a liquid or gas. Fiber lasers are in high demand in the metal cutting industry since they reduce consumable costs and can effectively cut a wide variety of materials. With a wavelength of merely 106 nanometers, fiber lasers are the ideal solution for cutting reflective metal materials, which is one of its key advantages of CO2. In addition, fiber lasers are known for their processing speed, minimal maintenance, low operational costs, increased reliability, performance, and efficiency, ultimately resulting in reduced cost and energy consumption.
Laser Cutting Machine Configurations
Generally, there are three different configurations used for laser cutting machines known as moving material, flying optics, and hybrid systems.
Moving material laser cutting machines feature a movable cutting surface onto which material is fixed, with the workpiece mechanically moved until desired cuts are achieved.
Flying optics feature a stationary workpiece with a movable cutter head, which moves across the workpiece to produce the necessary cuts. This configuration allows for faster processing times and is suitable for cutting materials of varying thickness and size.
Hybrid laser cutting machines combine qualities found in moving material and flying optics machines. Hybrid systems allow for consistent beam delivery at a reduced power loss and a greater capacity per watt than flying optics systems.
Similar Processes to CNC Laser Cutting
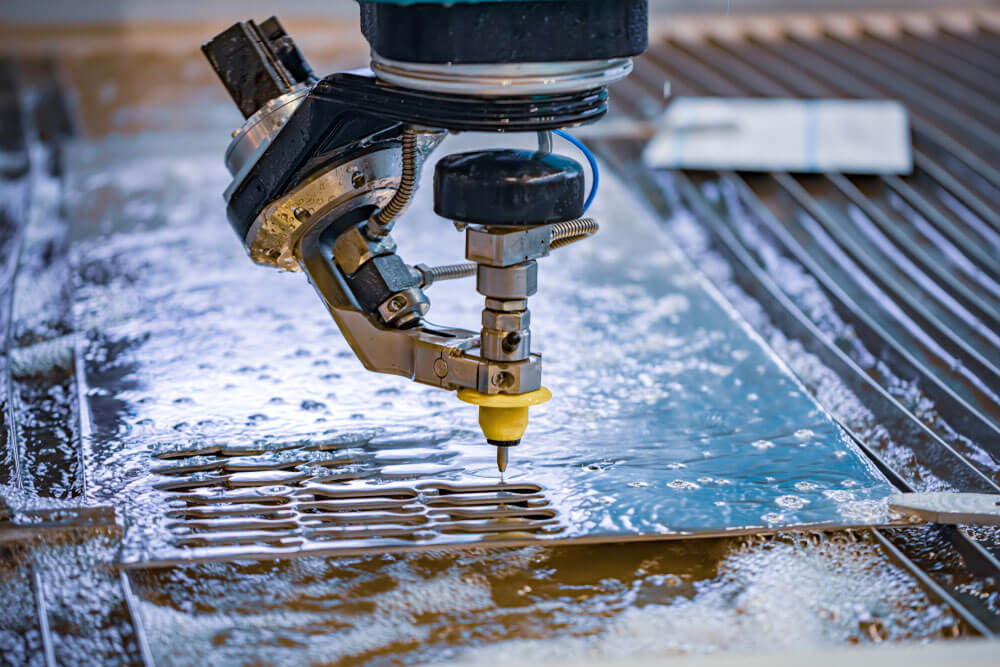
Waterjet Cutting
This mechanical cutting method mainly cuts sheet material into 2d parts using a high-pressure pump. This is achieved through a high-pressure, high-speed water stream, which forces water out of a waterjet cutting head. Materials that are challenging to cut, including metals, require an abrasive material to be added to the water to increase speed and heighten the cutting capacity. Materials and water lost during the cutting process are collected in a tank alongside the material. This process can cut a wide variety of materials beyond metals and does not emit hazardous fumes. Waterjet cutting cools the material being cut, which implies heat cannot impact the chemical and mechanical properties of the area being cut. It is however not ideal for thick cuts on hard metals, since metal width and hardness impact the cut speed, thereby reducing the quality of the workpiece being cut. It is also quite costly and requires lots of maintenance.

EDM
EDM wire-cut machines are suitable for intricate designs demanding high dimensional accuracy and edge quality, producing a better surface finish. The heat-affected area is smaller and there is more control over the process, resulting in less material damage. Laser cutting is much speedier though the heat-affected zone is larger and the cut edge is poorer in comparison to what EDM wire-cut machines can achieve.
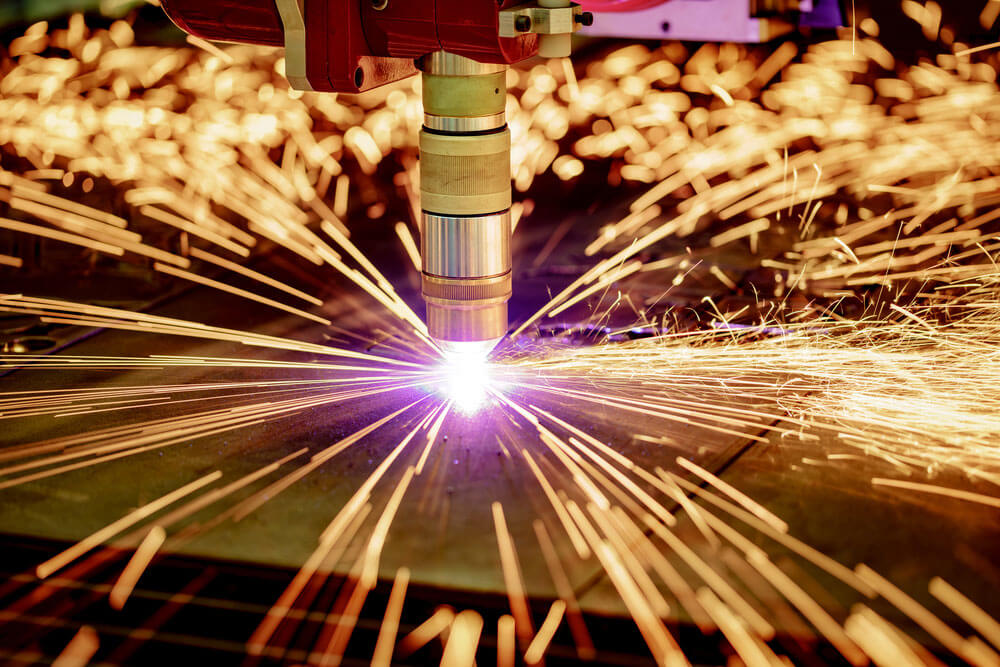
Plasma Cutting
Perfect for the production of 2d parts, plasma cutters use a high-velocity stream of ionized gas to cut through materials. Depending on the material in question, many gases can be used for plasma gas. Laser cutting of metals is more precise than plasma cutting, though most industrial lasers cannot cut at a width of metal thickness that plasma cutters can achieve. Plasma cutters are capable of cutting materials including steel plate.

Laser Cutting Versus Mechanical Cutting
Laser cutting is a streamlined and efficient process compared to mechanical cutting since the laser device does not come into direct contact with the workpiece, alleviating any potential contamination or damage to the material and equipment. Mechanical cutting includes a cutting edge, which can either become contaminated by the material or contaminate the material. The laser beam is not exposed to wear and tear, therefore there is a higher rate of precision and a lesser chance of warping the material being cut since lasers feature a small heat-affected zone. Another limitation of mechanical cutting is that certain materials are simply impossible to cut and require more innovative technologies. When choosing between a laser cutting service and mechanical cutting, keep in mind that various machine shops include the option to select a combination of the two cutting services, thereby utilizing the qualities of both processes without compromising quality or yielding additional costs.
CNC Laser Cutting Advantages
CNC Laser cutting is a versatile cutting method capable of cutting metal as well as being utilized as an acrylic laser cutting machine capable of cutting a variety of non-metallic materials that cannot be cut by Plasma processes. It has various advantages over Waterjet, EDM, and Plasma cutting methods. It requires less power due to its reduced heat-affected zone. CNC laser cutting results in minimal warping and has narrower kerf widths. It is accurate and includes faster processing and production times. 2d laser cutting parts are notably less costly to manufacture than 3d parts and can produce nearly any 2d shape.
CNC Laser Cutting Disadvantages
Limitations to metal thickness may occur since it is not suitable to cut very thick plates. Lasers could be very costly and result in high power consumption, depending on the heat input required, the desired thickness, the process used, and the cutting rate. The thermal cutting method, which melts the material, could result in dangerous fumes and gases being emitted.
The Future of Laser Cutting Technology Is Here
In many ways, CNC laser cutting services are the ideal choice when it comes to selecting a technology that is versatile and capable of cutting metal and non-metal raw materials with precision. The laser beam is capable of cutting virtually any contour rapidly and with flexibility. The need for additional post-processing operations is eliminated since CNC Laser technology is faster than more traditional techniques such as mechanical cutting and is superior in its function, which is precisely why it is the tool of choice in a wide range of industries.