Introduction to Milling
Since 1818, when the first milling machine was invented, milling machines have been further developed to feature excellent metal cutting capabilities and increased speed. Various types of milling machines are available and are used across a variety of industries. Milling machines can be operated manually or using CNC (computer numerical control). Milling is a machining process that shapes stock material through the use of rotary cutters most commonly on a moveable table. Milling machines carve out materials based on CAD design file. The machine spindle can be oriented vertically or horizontally. The cutter removes material and is capable of performing numerous complicated shapes. Milling encompasses various processes and machines and is among the most commonly used machining processes in the metalworking industry due to its ability to machine parts with precision and accuracy.
What is CNC Milling?
Before the invention of the first CNC milling machine in 1952, milling machines were manually operated. This process required manual labor to complete complex parts. Technological advancements have enabled industries to use CNC milling machines to complete customized products with greater efficiency, speed, and flexibility in order to meet customer demands. CNC milling machines are capable of performing various machining processes with impressive precision. This process accommodates a plethora of materials ranging in shape and size and reduces the impact of human error. CNC milling machines are useful for industrial and commercial production and are often used in the aerospace, electronics, and medical industries.
How do CNC Milling Machines Operate?
Most modern CNC milling machines contain both horizontal and vertical machining centers and operate on three to five axes, which enables them to perform with a higher degree of detail and precision. CNC milling machines use rotating cylindrical cutters which create slots, holes, and details in various materials by moving along multiple axes. They function without manual interference since they are equipped with automatic tool changers, coolant systems and tool carousels.
CNC Machining Materials
CNC machines can cut through virtually any material including plastics, such as acrylics and polycarbonate, or metals like steel, brass, copper and aluminum. To assure optimal machine configurations including the depth of cut, cutting speed, and feed rate, the properties of the material should be considered, including the toughness, strength, resistance to temperature, and cost-efficiency.
Types of CNC Milling Machines
Depending on the machining application, there are several milling machines available to choose from:
Knee-type
These types of milling machines contain a vertically adjustable work table and a fixed spindle. Depending on the machine tool position, the knee can either be raised or lowered on the column. There are two types of knee-type milling machines, vertical, which are fitted with large spindles and are used for the high production of smaller diameter circular parts, and horizontal, which are fitted with small spindles.
Ram-type
These milling machines feature a spindle mounted to a movable housing on the column, which enables the milling cutter to move forwards and backward in a horizontal plane. Two of the most popular ram-type milling machines are universal and swivel cutter head milling machines.
Bed-type
These types of milling machines contain a sliding table, which cannot be raised and is limited to longitudinal table movement only. The sliding table is mounted right onto the massive machine bed, preventing the raw materials from moving along the Y and Z axis. There are various bed-type milling machines available, some of which are simplex, which contain a single spindle moving along the X or Y axis, duplex, which contains two spindles, and triplex milling machines, which contain two horizontal spindles and one vertical. Bed-type milling machines are often used for the mass production of large and heavy machine parts and castings.
Planer-type
Planer-type milling machines are similar in function to bed-type milling machines since they contain work tables fixed onto a Y and Z axis, with a primary difference being their capability to support multiple machine tools simultaneously.
CNC Milling and Turning
CNC Milling
CNC machining is used in the manufacture of components for various industries. The most common type of CNC machining is milling. The milling process involves cutting tools that rotate and remove material from the stock to create holes, pockets and other shapes. The CNC milling process is versatile since it can process various types of metals, plastics, and wood to manufacture complex parts.
CNC Turning
CNC turning involves a spinning workpiece and a cutting tool that removes material. This is known as subtraction machining. CNC milling rotates the cutters instead of the workpiece.
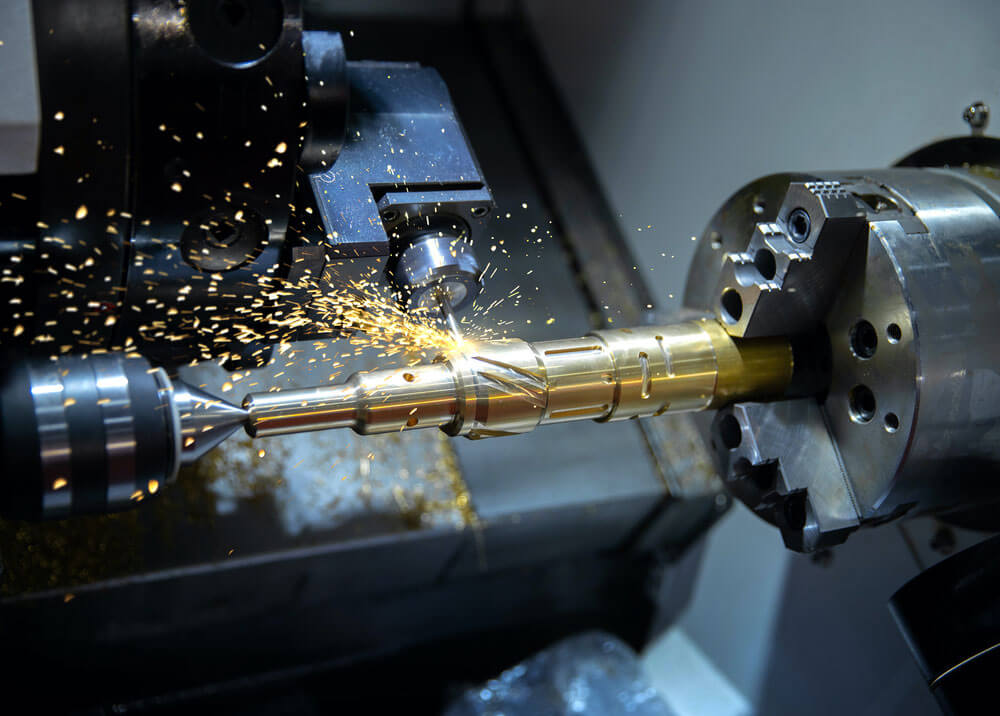

Production Capabilities of CNC Milling and Turning
CNC mills are primarily used for creating complex geometries, while CNC lathes can be used to create mainly cylindrical shapes. CNC milling is the better choice for machining flat and irregular surfaces. CNC turning mainly works on conical and cylindrical non-flat surfaces. CNC turning entails continuous cutting, as the tool remains in constant contact with the material. CNC milling involves intermittent cutting, as the cutting teeth engage and disengage from the raw material. CNC turning often produces parts faster and at lower cost in comparison to CNC milling. CNC milling produces custom-shaped components and is generally used for short to medium runs.
CNC Milling and Turning Applications
Applications of CNC milling can be found in various industries including:
Aerospace: CNC milling manufactures aerospace components using various. CNC milling is suitable for challenging materials to machine, such as Inconel, a nickel-chromium alloy that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressure.
Medical: Medical industries rely on CNC milling machines and lathes to create equipment and tools requiring precise and unique specifications.
Energy: The energy industry including solar energy, hydropower, and wind energy relies on CNC milling and turning to manufacture system components to provide continuous generation of power.
Military: The defense industry relies on CNC milling and turning techniques to mass-produce parts and prototypes.
Automotive: CNC machining is a popular choice for prototyping and milling auto parts. Many automotive suppliers depend on CNC machining services.
CNC Machining For Custom Car Parts
Many automotive industries rely on customization to meet specific customer needs and requirements. CNC milling and turning can be used in the creation of custom car parts that require precision and efficiency. CNC milling machines ensure that products are manufactured quickly without errors. CNC milling is fast and reliable and is capable of quickly creating various parts such as engine components.
CNC Machining For RC car parts
CNC machining is commonly used to create parts for RC (radio-controlled) cars, planes, and boats. The RC community is well known for its customization of many unique designs and upgrades. Hobbyists can design custom parts in CAD software so they fit custom builds to their exact dimensions. Finishing services, such as powder coating and anodizing, can allow hobbyists to further customize the parts to their liking.
CNC Machining Advantages
Precision: CNC machines function without manual intervention, reducing human errors. Software programs and codes assure that machines can manufacture accurately for product consistency. Cost-Effectiveness: CNC machines result in lower production costs since they produce minimal waste and do not rely on manual labor. In addition, they save energy by not using resources and labor beyond what is necessary.