CNC Turning Services
CNC lathes produce parts by feeding a cutting tool into rotating material.
eMachineShop offers a cost-effective turning services whether you need a single part, batch of prototypes, or a production order.
- 50+ Materials.
- FREE Shipping in the USA.
- 100% Quality Guaranteed.

Advantages of CNC Turning
- Economical for both short and long runs
- High dimensional tolerances are possible
- Smooth finishes can be achieved
Design Recommendations for Turned parts
- Avoid designing long, thin structures
- Consider specifying a desired surface roughness
- Bored holes become difficult when the ratio between depth and diameter is high
What is CNC Turning?
Turning is a process by which material is cut to create round shapes, typically using a CNC Lathe. The workpiece is placed inside the lathe and rotates while a cutter removes material until only the desired shape remains.
Turning is ideal for cylindrical parts and is primarily done using round rod material, but square and hexagonal bar stock can also be used.
The primary objective of CNC turning is to machine parts having shapes that can be formed by feeding a cutter into a rotating bar of raw material. Turning can also be used to reduce the diameter of a workpiece to a desired dimension. Lathe turning is mainly used for shaping metal or wood. CNC lathes are commonly used in metalworking, woodworking, and metal spinning processes. CNC lathes produce accurate round shapes, often with precision outer diameter (OD) and inner diameter (ID).

eMachineShop Turned Parts
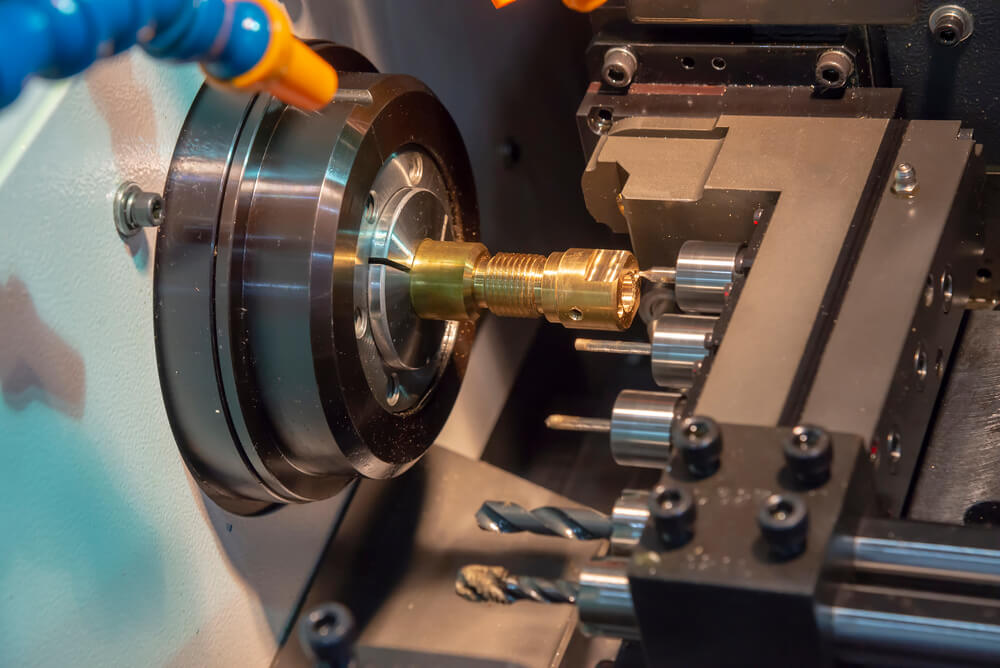
CNC Turning Machine Process
The initial step of the CNC turning process involves the preparation of a CAD file, which is then converted to a CAM program – a program written in the G-Code language. Next, a set of tools is mounted on the tool changer. For example there could be:
- a right-hand turning tool
- a left-hand tool
- a grooving tool
- a drill
- a tap and
- a parting tool.
The machinist may then mount in a chuck the raw bar material to be turned. A run of one piece may be done next to verify that the tools and the CAM program are set up correctly. The first-article part is then inspected. Any setup refinements can then be made. Production then begins. In some CNC turning systems bar material can be loaded automatically via a bar feeder. This is particularly helpful in large quantity runs.

Benefits of CNC Turning

CNC turning service has numerous benefits including high accuracy and precision. This assures that turned parts are created to meet exact specifications while eliminating the possibility of human error. CNC lathes produce minimal defects and achieve faster results compared to their manual counterparts.
Raw materials
CNC lathe machining can produce high-quality parts with accuracy and precision in a variety of raw materials. The CNC turning process can be applied to most hard materials and metals such as:
- Aluminum
- Stainless Steel
- Stainless
- Brass
- Copper
- Titanium
- etc.
Lathe Tooling
Lathes are among the most versatile machine tools available and are used for streamlining various machining operations. The most common lathe machining operation is turning which primarily removes material on the outside diameter of the raw bar material which is held in a rotating chuck.
Design tips
When designing parts to be CNC turned consider these tips:
- If practical, choose an outside diameter (OD) that is slightly smaller than a standard bar size. For example, avoid specifying an OD of 0.5”.
- Avoid sharp corners – use a radius instead.
- Avoid flimsy shapes that will deflect due to cutting pressure
- Avoid shapes that have a high length to diameter ratio. 2 or 3 to 1 is optimum but much higher ratios are possible with proper tooling. Very long thin parts in CNC turning can be processed with a steady rest – a clamp-like device that supports the part from the outside to reduce vibration.
- Avoid deep precision holes. Holes with high length to diameter ratio may require the use of a “boring bar” when tolerance is high. However such tools can deflect if the length to diameter ratio is high. Such holes start to become more challenging at around 10:1.
Turning services provide two types of turning operations, rough and finish:
- The objective of rough-cut is to remove the bulk of unwanted material
- Finish turning is used to improve surface finish, tolerance, and dimensional accuracy.
Additional functions include:
- Drilling to create holes typically at the end of a bar
- Tapping to create threaded holes
- Grooving to create grooves on the OD or ID.
- Parting tools that cut the machined part off of the bar
- Reaming
- Facing
Aluminum CNC turning parts
Aluminum CNC turning parts are custom machined parts made using a CNC turning center, a type of CNC machine that rotates a workpiece while cutting it with a single-point cutting tool. The use of CNC turning centers allows for precise and accurate machining of aluminum parts, with the ability to create complex shapes and features. These aluminum parts can be used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical, where precision and reliability are critical.
Single point threading
Single point threading in CNC turning is a process by which a cutting tool is used to cut a helical thread into the workpiece. This can be an external or internal thread. The cutting tool is moved in a synchronous fashion along the surface of the workpiece while the spindle rotates. This creates a threaded groove over the length of the workpiece. The depth and angle of the groove depends on the shape of the cutting tool, the feed rate, and the spindle speed. The final thread is formed by advancing the cutting tool along the groove until the required thread depth is achieved.

Lathe components
Chuck
A CNC lathe machine has a chuck used to hole the rotating raw material bar. Most chucks have 3 or 4 jaws. Three jaw chucks are typically faster to setup for round materials. Four jaw chucks are more flexible as they can hold round and rectangular bars but are more time consuming to set up.
Carriage
CNC lathes have a carriage, which is located between the headstock and tailstock and which guides the tool to cut the workpiece.
Tailstock
Short parts can be held in a chuck without support for the end protruding from the chuck. When parts have a length much greater than their diameter, the protruding end needs support to avoid flexing and vibrating. That is the function of the tailstock. The tailstock holds the free end of the workpiece – often by a simple cone shaped point that sits in a cone shaped hole at the end of the rotating workpiece.
Headstock
The key component of a CNC machine is the headstock which supports the mechanism that rotates the workpiece.
CNC Lathe Bed
The CNC lathe bed is a beam used to support other components of the lathe, including the headstock and tailstock.

CNC Turning Applications
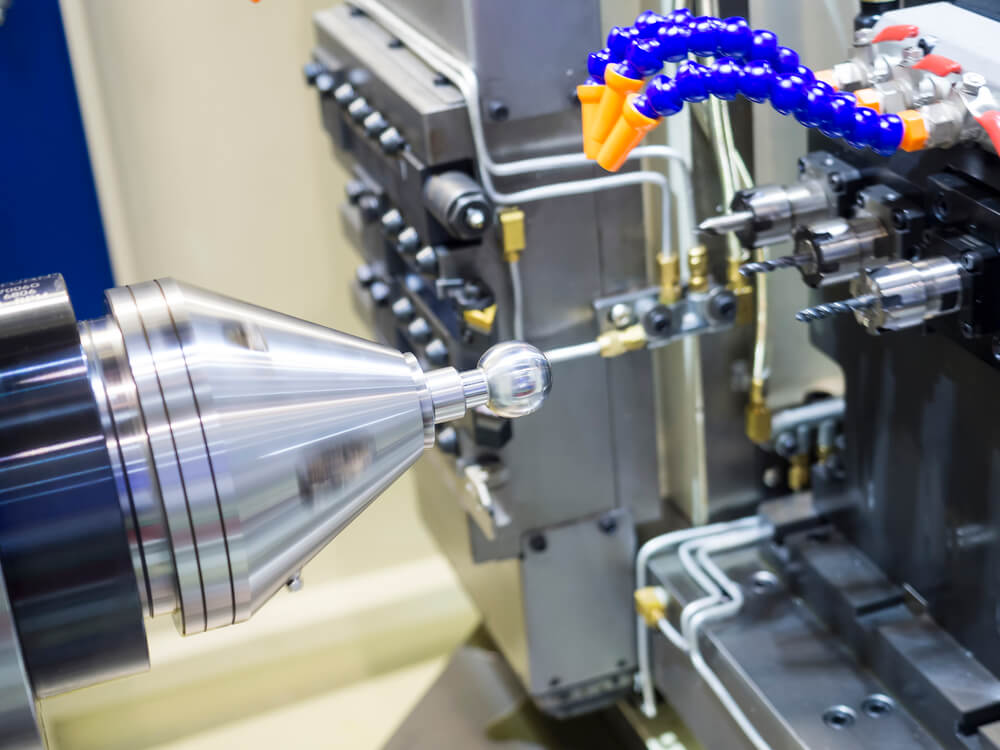

- Transportation: Some of the main transportation sectors that depend on CNC turning services for the creation of transportation equipment include the aerospace, automotive, mass transit, rail and locomotive, military, and trucking industries. CNC machines are used for designing transportation equipment such as headnuts, gear blanks, bearing blocks, levers, axles, and rotors.
- Construction: The construction industry demands components that are capable of handling heavy parts. CNC machines in construction are often used to create bolts and screws from an array of metals such as stainless steel and aluminum, that are used in assembly and fastening functions.
- Vehicles: CNC turning services are used for auto parts including parts for engines, such as cylinder heads, connecting rods, and camshafts; transmission parts including shafts, and rings; suspension components like sway bars, control arms, and tie rod ends; plus other items such as bushings and bolts.
- Air Travel: The aviation industry relies on CNC turned parts for the customization and creation of probes, joint connectors, fasteners, as well as engine and aircraft components. Many aviation based parts use titanium due to its ability to handle extreme high and low temperatures.
Accuracy
CNC lathes are highly accurate and precise machining tools, especially with hard materials such as steel, aluminum, stainless, titanium, brass, and copper metals. Plastic materials can also be used with CNC turning machining but due to the properties of the plastic materials, the achievable tolerance is usually lower than their metal counterparts and are more prone to deformation when machined. Plastic materials are also less expensive than metals which in some cases makes plastic a more popular choice for certain cases.
CNC turning machines typically provide accuracy and repeatability to within a few thousandths of an inch. With proper equipment and setup, CNC lathes can attain tolerances up to a few ten-thousandths or even better, however at that level, the temperature of the material comes into play as does the quality of the machine and the geometry of the part being machined.
Bar feeders
Bar feeders are used on CNC turning machines to automate the material handling process. They are designed to feed a continuous length of bar stock into the spindle of the CNC turning center. This saves labor and hence cost for high volume jobs. It also shortens the delivery time.

Geometries

The CNC turning machining process is capable of achieving both simple and complex geometric designs with a variety of added features. Common part shapes that are possible on a conventional CNC turning center include:
- Straight cylindrical shapes
- Tapered shapes such as a cone
- Contoured shapes such as a chess pawn
- Shapes with threaded holes
- Shapes with grooves such as for o-rings
- Knurled shapes such as for handles
- Chamfered shapes
- Shouldered shapes
Manufacturing advanced designs with both turning and milling features
CNC turning and CNC milling are two of the most common machining processes used to create custom machined parts. While CNC turning machining uses a lathe to rotate a part against a cutting tool to create a cylindrical shape, CNC milling machining uses a cutting tool that rotates around an x, y, and z axis to create a three dimensional shape. Some advanced 3D CAD models may have both turning and milling features included so the two manufacturing processes are combined in sequential steps to machine the raw material into an accurate and quality production run.
Secondary surface finishing processes
CNC lathe production can involve a variety of secondary finishes to ensure that the metal parts meet the desired surface quality after they have finished the machining process A secondary finishing service can include deburring, grinding, polishing, anodizing, painting, and plating. Deburring helps to remove any sharp edges or burrs, while grinding and polishing can improve the surface finish of the metal. Anodizing and plating can improve the strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of the metal, and painting or powder coating, if the machined part is metal, can be used to add color to the part.
Choosing a CNC turning manufacturer for your next project
When choosing a CNC turning manufacturer for your project, it is important to consider the quality of the parts they produce, the secondary surface finishes they can accommodate, their turnaround time, and their customer service support. It is important to make sure that the manufacturer is up to date on the latest technology and has the necessary CNC machines to produce the parts you need in a cost-effective and reliable production run. Additionally, it is important to make sure that the manufacturer is experienced in the types of machining the CAD design may require such as tooling components, raw material acquisition, and access to a CNC milling machine to accommodate any advanced features. Finally, you should make sure that the cost of the parts is within your budget and is competitive with other quotes you have received.